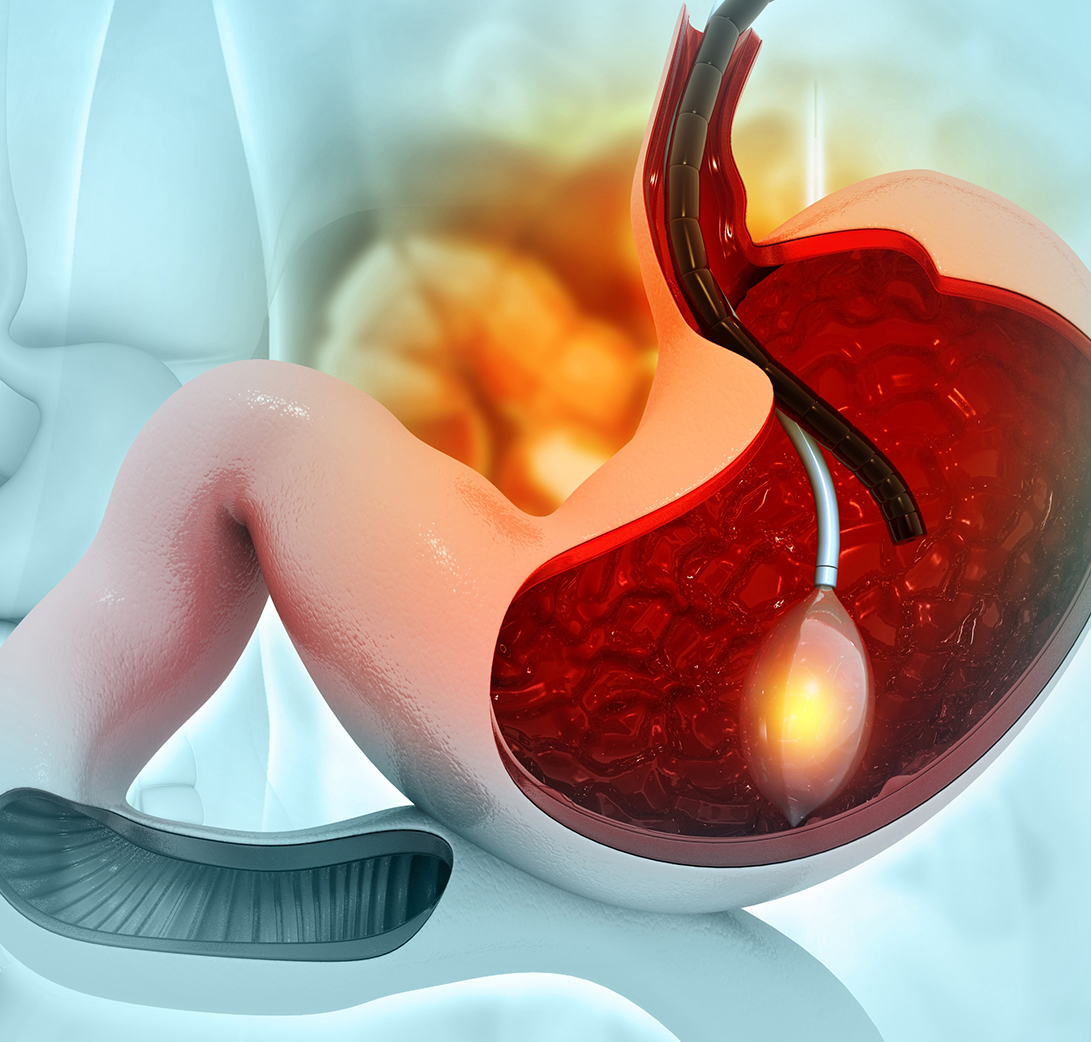
What Is a Gastroscopy?
Gastroscopy, also known as upper gastrointestinal (GI) endoscopy, is a minimally invasive diagnostic and therapeutic procedure used to examine the upper part of the digestive system.
It involves the use of a thin, flexible tube called an endoscope equipped with a light and camera. The endoscope is gently passed through the mouth, down the esophagus, and into the stomach and the first part of the small intestine (duodenum).
This procedure provides doctors with a clear view of the inner lining of these organs, enabling them to identify abnormalities, diagnose conditions, and perform treatments without the need for surgery.