A hernia occurs when an internal organ or tissue pushes through a weak spot in the surrounding muscle
or connective tissue. This often results in a noticeable bulge or lump under the skin. Hernias can
develop in various parts of the body and are commonly associated with areas where muscles have been
strained or weakened over time.
Hernias can result from a variety of causes, including heavy lifting, chronic coughing, obesity,
pregnancy, or prior surgeries. Some individuals may also have a genetic predisposition to hernias due
to naturally weaker connective tissues.
While hernias are generally not life-threatening, they can cause discomfort, pain, and, in severe
cases, lead to complications such as strangulation, where the blood supply to the herniated tissue is
cut off.
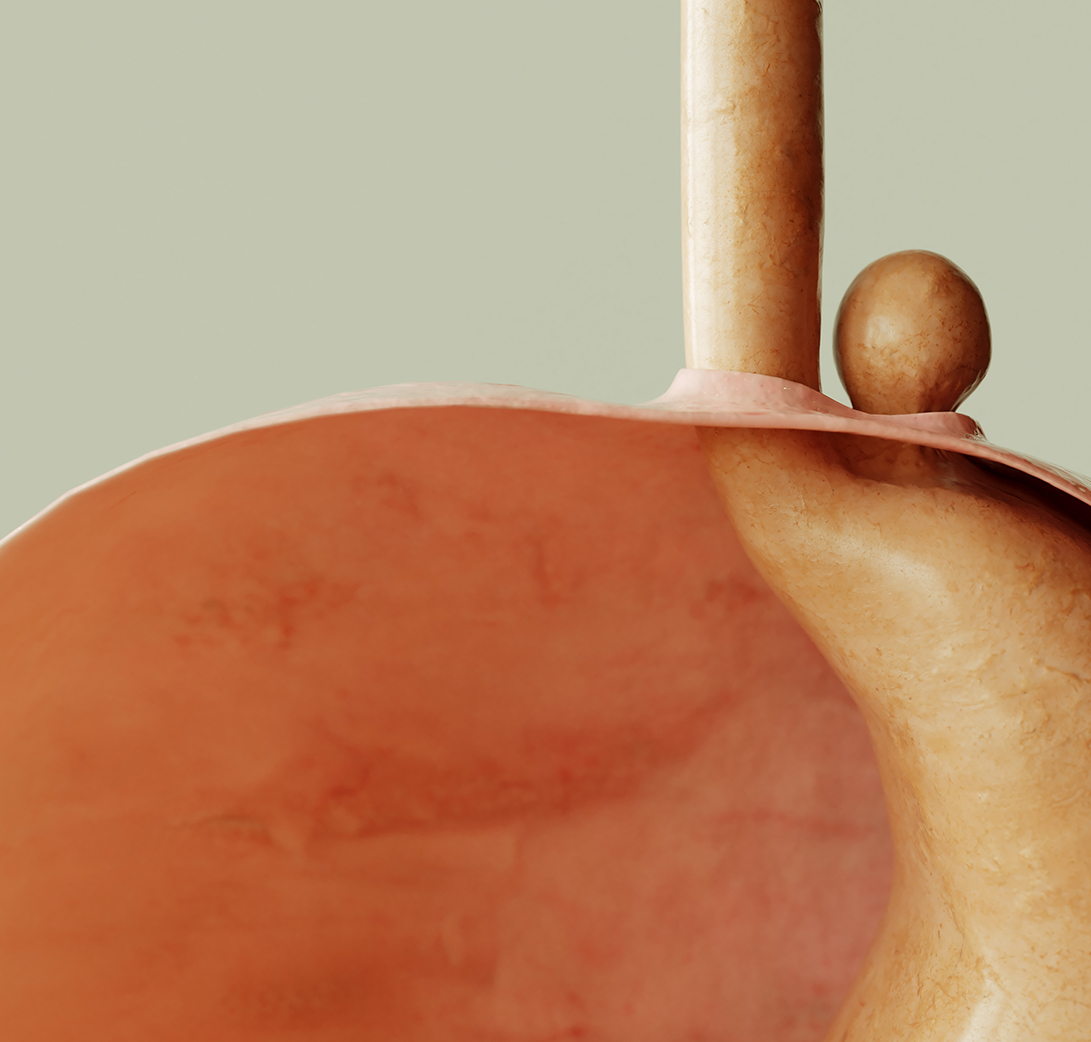
Hernias can occur in different parts of the body, and the type of hernia often determines its symptoms and treatment options. Here are the most common types:
Inguinal hernias are the most prevalent type and primarily affect men. They occur when a portion of the intestine or fatty tissue protrudes through a weak spot in the inguinal canal, located in the groin. This type often presents as a bulge in the groin area, which may become more pronounced when standing or coughing.
Less common than inguinal hernias, femoral hernias are more likely to affect women, particularly those who have been pregnant. They occur when tissue pushes through the femoral canal, located just below the groin.
Umbilical hernias occur around the navel and are common in infants, though they can also affect adults. In babies, this condition often resolves on its own as the abdominal muscles strengthen. However, in adults, surgical repair is usually necessary if the hernia becomes symptomatic.
Hiatal hernias occur when a portion of the stomach pushes through the diaphragm into the chest cavity. This type is often associated with symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), such as heartburn and difficulty swallowing.
These hernias develop at the site of a previous surgical incision where the abdominal wall has been weakened. They can occur months or even years after surgery and are more common in individuals who are overweight or have undergone multiple abdominal surgeries.
Epigastric hernias appear in the upper abdomen, typically along the midline between the navel and the chest. They often consist of fatty tissue and are usually small, but they can still cause discomfort.

While small, asymptomatic hernias may not require immediate treatment, larger or symptomatic hernias often need medical intervention.
- Watchful Waiting:For small hernias that cause no pain or discomfort, doctors may recommend monitoring the condition regularly.
- Lifestyle Changes:Maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding heavy lifting, and treating chronic cough or constipation can help prevent hernias from worsening.
- Supportive Devices:Trusses or belts may provide temporary relief by supporting the hernia, though they do not address the underlying issue.
Surgery is the most effective way to treat hernias and prevent complications. The two primary surgical techniques are:
- Open Hernia Repair:In this traditional approach, the surgeon makes an incision near the hernia, pushes the protruding tissue back into place, and reinforces the weakened area with sutures or a synthetic mesh. Open surgery is often performed under local, regional, or general anaesthesia, depending on the hernia's size and location.
- Laparoscopic Hernia Repair:Laparoscopic surgery involves making small incisions and using a camera-guided instrument to repair the hernia. This method offers several advantages, including shorter recovery time, less pain, and minimal scarring.
- Robotic-Assisted Surgery:Robotic-assisted hernia repair is an advanced form of laparoscopic surgery that provides enhanced precision and control. Surgeons use robotic instruments to perform the repair, resulting in even greater accuracy and reduced trauma to surrounding tissues.

Recovery times vary depending on the type of surgery performed and the patient's overall health. Most patients can resume light activities within a few days of laparoscopic surgery, while recovery from open surgery may take a few weeks. It is important to follow post-operative instructions carefully, including avoiding heavy lifting and strenuous activities until one is fully healed.

We understand your anxieties and our team is here to support you throughout your health journey through our comprehensive screening services, diagnostic tools and treatment plans.
| Tel | : | +65 6908 6106 |
| Fax | : | +65 6908 6107 |
| : | +65 8022 2866 | |
| : | drtoh.eelin@gmail.com |
| Mon-Fri | : | 8:30am - 12:00pm2:00pm - 5:00pm |
| Sat | : | 8:30am - 12:00pm |
| Sun & PH | : | Closed |

